In this blog post I’ll show how to surface data from external systems in SharePoint 2013 using Managed Navigation and Content By Search web parts. For instructions on how to crawl external systems using BCS, External Content Types and SharePoint Search, refer to my previous blog post: Business Connectivity Services, External Content Types and Content By Search in SharePoint 2013 – Part 1.
Managed Properties
In order for us to be able to use different Product and ProductModel external content type fields, we need to create a number of managed properties. For this example, the following managed properties need to be created:
- Navigate to Central Administration > Manage service applications > Search Service Application
- Click the Search Schema link in the Queries and Results side navigation section
- Click New Managed Property to create a new managed property for each of the items below
- ProductModelSummary
- Name: ProductModelSummary
- Type: Text
- Searchable: True
- Retrievable: True
- Safe: True
- Crawled property mapping: vProductModelCatalogDescriptionRead
ListElement.Summary
- ProductModel
- Name: ProductModel
- Type: Text
- Searchable: True
- Queryable: True
- Retrievable: True
- Safe: True
- Crawled property mapping: vProductAndDescriptionRead
ListElement.ProductModel
- ProductDescription
- Name: ProductDescription
- Type: Text
- Searchable: True
- Retrievable: True
- Safe: True
- Crawled property mapping: vProductAndDescriptionRead
ListElement.Description
- CultureID
- Name: CultureID
- Type: Text
- Queryable: True
- Safe: True
- Crawled property mapping: vProductAndDescriptionRead
ListElement.CultureID
- ProductID
- Name: ProductID
- Type: Integer
- Queryable: True
- Safe: True
- Crawled property mapping: vProductAndDescriptionRead
ListElement.ProductID
- Click the Content Sources link in the Crawling side navigation section
- Start Full Crawl for the AdventureWorks2012 content source
Result Sources
The next step is to create two new result sources on the publishing site that we can use later to configure content search web parts.
- On the publishing site, navigate to Site Settings > Search Result Sources
- Click New Result Source to create each of the result sources below
- Product
- Name: Product
- Query Transform: {searchTerms} contentsource:AdventureWorks2012 entityname:Product cultureid:en
- ProductModel
- Name: ProductModel
- Query Transform: {searchTerms} contentsource:AdventureWorks2012 entityname:ProductModel
Site Navigation
Now let’s confirm that managed navigation is enabled and configured on the SharePoint site. It is enabled for new publishing sites by default in SharePoint 2013.
- Navigate to Site Settings > Look and Feel > Navigation
- Make sure that Managed Navigation is selected for both Global Navigation and Current Navigation
Pages
We’ll need to create 3 new pages on the site – one top-level page listing all product models, one page that will list all products for a product model, and one page to display product details.
The first page has to be created by using the Site Actions > Add a page option so that SharePoint automatically creates and configures the navigation term.
- Create a new page called Products by going to Site Actions > Add a page
- Navigate to the Pages document library on the site
- Create a new page called Product by using the New Document option in the ribbon
- Create a new page called Product-Model by using the New Document option in the ribbon
Managed Navigation
Now is the time to configure the managed navigation to use the pages created earlier.
- Navigate to Site Settings > Site Administration > Term store management
- Expand the Site Collection node
- Expand the Site Navigation node
- Select the Products term
- Select the Term-Driven Pages tab
- Change target page for children of this term
- Change Catalog Item Page for this category and Change Catalog Item Page for children of this category to use the Product.aspx page
- Press Save to commit the changes
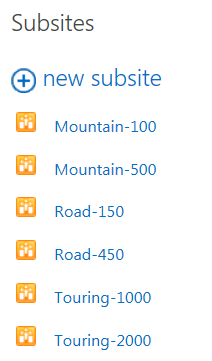
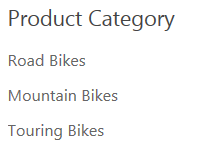
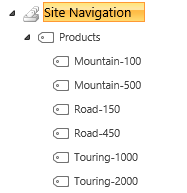
- Add a child term to the Products navigation term for each of the product model. No settings need to be customized for the child terms.
- Mountain-100
- Mountain-500
- Road-150
- Road-450
- Touring-1000
- Touring-2000
The navigation term set should now looks similar to this:
Content By Search
The final steps is to add and configure content search web parts to the pages we created earlier.
- Click the Products link in the global navigation to navigate to the Products.aspx page
- Edit the page and add a Content Search web part from the Content Rollup category
- Edit web part properties
- Press Change Query to bring up the Query Builder user interface
- On the Basics tab, switch to Advanced Mode, select ProductModel result source in the dropdown and clear the Query text
- Press OK to close the query builder
- Change the Number of items to show to 6
- In the Display Templates section, select Two lines as the Item display template
- In the Property Mappings section, select ProductModelSummary as Line 2
- Press OK to apply changes and save the page
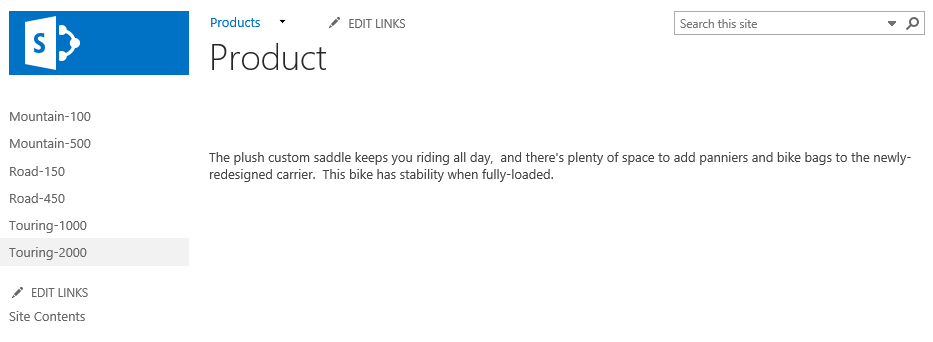
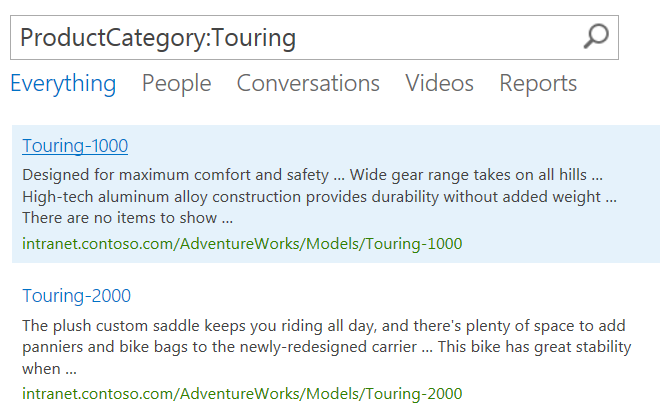
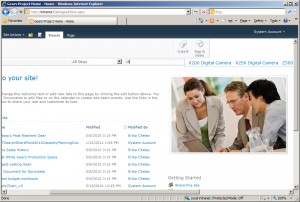
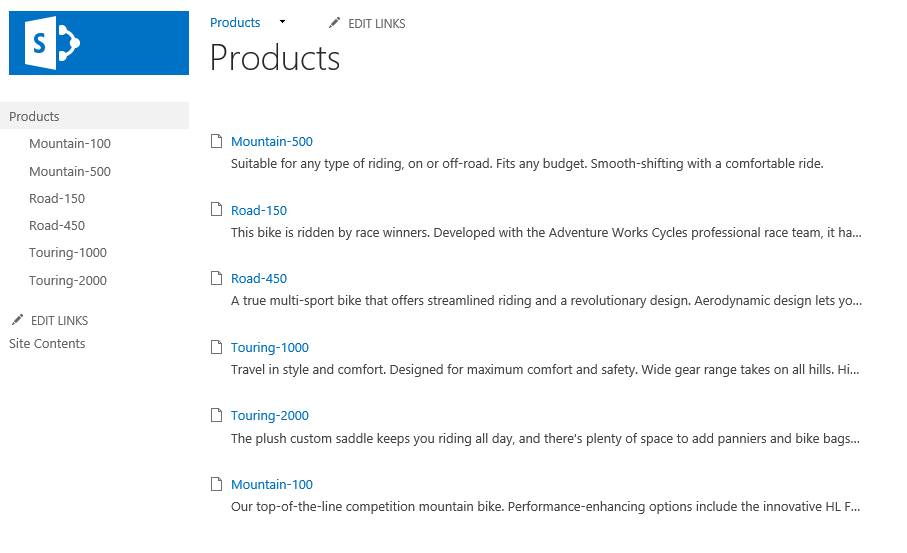
The Products page should now look like this:
Next, click one of the links on the page to navigate to the product model page.
- Edit Product-Model.aspx page
- Add a Content Search web part from the Content Rollup category
- Edit web part properties
- Press Change Query to bring up the Query Builder user interface
- On the Basics tab, switch to Advanced Mode, select Product result source in the dropdown
- Set Query text to productmodel:{Term.Name}
- Press OK to close the query builder
- Change the Number of items to show to 10
- In the Display Templates section, select Two lines as the Item display template
- Press OK to apply changes and save the page
Your Product Model page should now look similar to this screenshot:
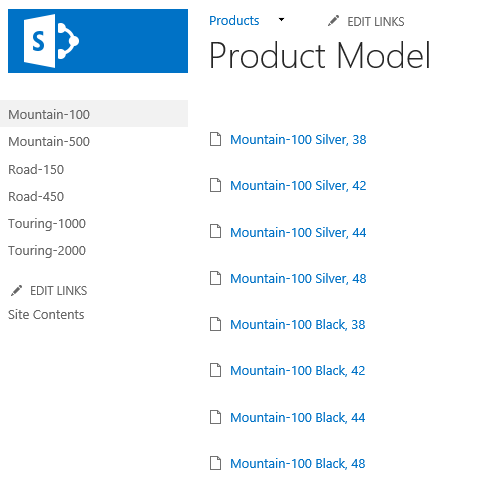
Now follow one of the links on the page to navigate to the product detail page.
- Edit Product.aspx page
- Add Catalog-Item Reuse web part from the Search-Driven Content category
- Edit web part properties
- Press Change Query to bring up the Query Builder user interface
- On the Basics tab, switch to Advanced Mode, select Product result source in the dropdown
- Set Query text to productid:{URLToken.1}
- Press OK to close the query builder
- In the Property Mappings section, select ProductDescription managed property
- Press OK to apply changes and save the page